Media Effects Research Lab - Research Archive
The effects review modality and genre on perceived source credibility of video games reviews
Student Researcher(s)
Richard J. Wirth (Ph.D Candidate);
Carly Chiavaroli (B.A. Candidate);
Faculty Supervisor
This paper was based on a project as part of the “COMM 506: Research Methods in Communications” course.
INTRODUCTION
Product review source, and message analyses feature predominantly in e-commerce literature, but questions persist about the effects of product review modality on consumer perceptions. In addition, video games research has not adequately addressed the impact of video game reviews on the games industry and audiences. The current research attempted to address the gaps presented in either body of literature by “reviewing” the effect of product review modalities (video, audio, and text) and game genre, on perceived source credibility of video game reviews.
RESEARCH QUESTION / HYPOTHESES
RQ 1: For the general population, what is the relationship between review modality, genre and perceived source credibility of the video game review?
RQ 2: For the general population, what is the relationship between review modality, genre, and perceived trustworthiness of the video game review?
RQ 3: For the general population, what is the relationship between review modality, genre, and attitudes toward the video game review?
H1: Review modality and Genre will be significantly related to game reviews’ perceived source credibility.
H2: Narrative Involvement will be higher in the video modality condition than in audio, which will be higher than the text modality, across all genres.
H3: Review modality will have a significant effect on participant distraction, moderated by genre.
H4: Message credibility will be perceived as higher for the video condition than for audio, and text will have the lowest message credibility.
H5: Review modality will have a significant effect on participants’ attitudes towards the reviews, moderated by genre.
METHOD
Describe your research method in a small paragraph. Please include all pertinent information.
A 4 (Genre: First-Person Shooter vs. Action-Adventure vs. Strategy vs. Storytelling) x 3 (Review Modality: Video vs. Text vs. Audio) fully factorial, between-subjects online questionnaire experiment was conducted to test the effect of Review Modality and Genre on perceived Source Credibility, Message Credibility, Narrative Involvement , Attitude towards the reviews, Distraction, and Enjoyment of web experiences. Participants were recruited online using Amazon Mechanical Turk, in exchange for monetary compensation (N = 499). Participants were randomly assigned to a genre and modality condition, and were presented with a video, audio or text type of review. Each type of review modality contained 3 different game titles, categorized under one genre, for a total of 12 games in all (Example: Action Adventure-Witcher 3, Rise of the Tomb Raider, and Uncharted 4).
RESULTS
Please describe your results in a paragraph here. If including tables, add table number and table title.
A 2x2 Factorial ANOVA on Source Credibility showed that Review Modality had a significant main effect F (3, 431) = 7.80, p < .01. However, Genre did not show a significant effect F (3, 431) = 1.96, p < .12. H1 was therefore partially supported. The difference between Video (M = 5.13, SE = 0.06) and both Text (M = 4.81, SE = 0.07) as well as Audio (M = 4.93, SE = 0.06) were significant.
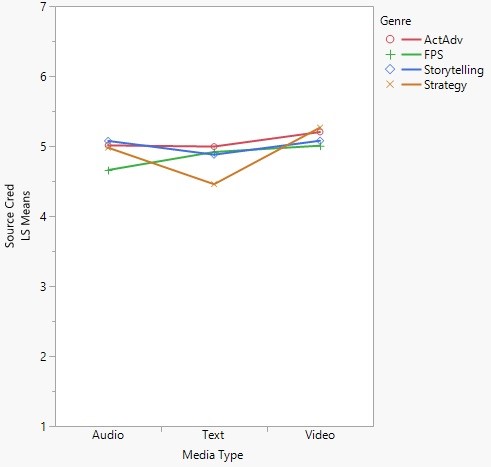
Figure 1. The interaction effects of Genre and Modality on Source Credibility
While Genre not make a significant difference in participants’ perceived source credibility, there was a significant interaction effect between Modality and Genre, F (6, 431) 2.95, p < .01. Review Modality had significant main effects on Narrative Involvement F (2, 431) = 14.76, p < .01, Distraction F (2, 431) = 5.83, p < .01, and Attitude toward the review F (2, 431) = 3.52, p < .05. Given these results, H2 was partially supported, and H3 was confirmed. H5 was fully supported: review modality, moderated by genre, had a significant effect on participants’ attitude towards the review stimuli.
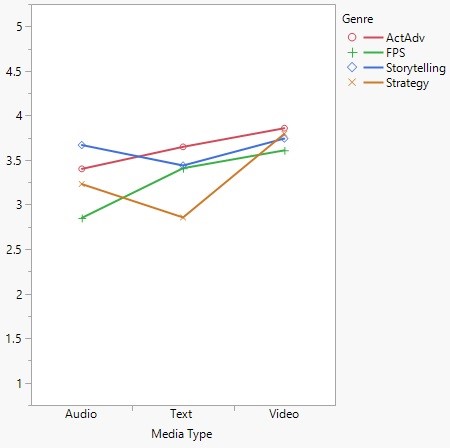 Figure 2. Graph of the interaction effects of Genre and Modality on Review Involvement
Figure 2. Graph of the interaction effects of Genre and Modality on Review Involvement
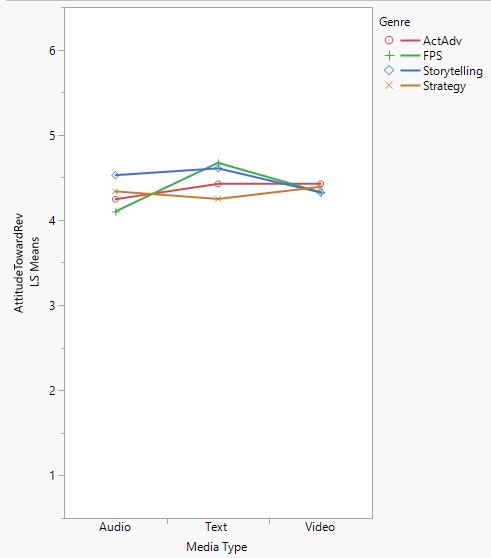
Figure 3. Graph of the interaction effects of Genre and Modality on Attitude towards the review
CONCLUSIONS/DISCUSSION
Honing in on the modality of the video game review revealed many differences for the level of perceived credibility, attitude, distraction, and narrative involvement. However, these differences were not always uniform across genre, or in a consistent order of effects. Genre was revealed to be a strong moderator of the differences in review modality, particularly for Strategy and FPS game genres. This study demonstrates that there is still more to learn about the nature and efficacy of product reviews in general. Concerning the video game industry and research field; as video games become increasingly successful in terms of market share, and the landscape of online reviewing changes to adapt to Web 2.0, it is crucial that media companies know the best strategies for connecting with their customers. The results of this study lend some support for visual media as the most appropriate reviewing tool for a product that is mostly visual and experience driven in nature (like a video game). Though maintaining content equivalency was a goal of the present study, future research should expand the exploration of genre and modality to include multiple review sites and structures.
For more details regarding the study contact
Dr. S. Shyam Sundar by e-mail at sss12@psu.edu or by telephone at (814) 865-2173

